Rectovaginal Fistula
What is rectovaginal fistula?
Rectovaginal fistula is formed between rectum and vagina due to unusual epithelial-lined formation. It is initiated at beneath the large intestine. In this condition due to the generation of passage, the fecal material and gas can even pass through the vaginal route.
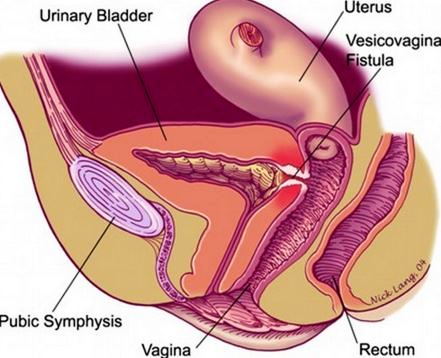
Picture 1 – Rectovaginal (obstetric) Fistula
The patient feels embarrassing because of the symptoms of this condition. The rectovaginal fistula is manageable with proper treatment. Treatment plan varies with individual to individual depending upon the size, site and etiology of the fistula.
Symptoms
The following are the major symptoms of the rectovaginal fistula:
- Vaginal discharge: Faecal material and gas are discharged through the vaginal route. In severe case, pus is also passed away from vaginal route.
- Foul smell: The vaginal discharge is having a typical foul smell which embarrasses the affected female.
- Frequent onset of infection: Genital organs frequently get infected; as stool excretion occurs through the vaginal route.
- Pain and irritation: Patient often complains pain and irritation at the junction between vagina and rectum.
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse: Patient also reported pain generation during sexual intercourse which also hamper their quality of life.
Causes
Traumatic mechanism is mainly responsible for the development of rectovaginal fistula. During labour pain using the episioproctotomy for childbirth causes perineal lacerations and that can be a reason of rectovaginal fistula. Perineal laceration is conducted in vaginal delivery. The infection of perineal lacerations also augments the development of the rectovaginal fistula.
Delayed labour causes increment of the pressure on the rectovaginal septum can produce necrosis and result in RVF.
Diagnosis
For diagnosis, initially physical examination is conducted and depending upon the severity of the condition, requires diagnosis procedure are decided.
Physical examination
The aim of the physical examination is the identification of the site of the fistula development and also checking the presences of tumour or infection. For determination of this, it is very necessary to physical examination by gloved hand of the peritoneum area (the area between the vagina and the anus). If the location of the fistula is inside the distant part, then may gloved hand cannot examine. In that case, speculum or proctoscope instruments may need to check the peritoneum.
Depending upon the physical examination following are the tests:
Contrast tests
If the fistula is located in the upper rectum, then barium enema helps to identify the location. By using, X-Ray contrast images can get a clear view of the fistula and confirming the particular location of the fistula either in the vagina or in the bowel.
Blue Dye test:
Insertion of tempons inside the vagina and injecting the blue dye via the rectal route helps to detect the fistula, as blue staining helps to locate the vagina.
Computerized tomography:
For confirmation about the location and size of the fistula it is necessary to conduct CT scan, as X-ray images are not always clears the findings.
MRI:
Some doctors also prefer to conduct MRI and then MRI can help to identify the location of the fistula. If the tumor is associated, then helps to determine the size and generated pressure of the tumor is also measured through MRI.
Anorectal ultrasound:
To get a video image of anus and rectum, ultrasound waves are used. Wand-like instrument is inserted into the anus and rectum to produce an image. By obtaining this image, anal sphincter image can obtain and also estimates may any injury present at the sphincter caused during childbirth.
Anorectal manometry:
This test is conducted for checking the rectal and anal sphincter functioning, this test is useful for planning the treatment procedure, as it analyzes stool controlling power.
Other tests:
The following tests are conducted depending upon the patient condition.
Colonscopy: Doctor may order a colonscopy, for obtaining the view of colon.
Biopsy: For confirmation of Crohn’s disease, the biopsy is conducted.
Treatment
The following are the treatment plan can be conducted:
Conservative Management
In this management plan, controlling of diarrheal discharge is conducted. This can help to augment healing, though this process is mostly applicable after surgical intervention for quick wound healing.
General Principles
This is also conducted before surgical repairing. Before a surgical intervention, it is necessary to treat patients with antibiotic therapy or immunosuppressive treatment for controlling the infection or self development of the disease. Usually these therapies are recommended before 3 to 6 months of the surgery, but if associated tissues does not get affected that much then may this treatment is not required.
Surgery/repair
Surgical repair procedures have the following option:
- Suturing of the fistula or provides the biologic tissue can allow fistula for fast healing.
- Tissue grafting from associated organ can help to develop new sets of tissue generation and fistula opening is flapped.
- Complex surgical repair is also required for Crohn’s disease or in the case of radiation damage.
- Colostomy is the process where the route of stool passage is diverse from rectal to abdominal. This is a complex process, it is recommended when faecal material passage worsens the rectal infection or a cancerous tumour or an abscess is delayed.
Complications
The associated complications which influence the development of the rectovaginal fistula are:
- Radiation therapy, which can cause injury at the junction between vagina and rectum
- Crohn’s disease is an example of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD and in chronic untreated situation influences the development of the RVF.
- Surgical trauma
- Frequent incidence of infection
- Neoplasm
Pictures


Picture 3 – Recto Vaginal Fistula
References
- Rectovaginal fistula Symptoms – Mayo Clinic at http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rectovaginal-fistula/basics/symptoms/con-20034033
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/193277-overview
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/193277-treatment
- Urology and Gynecology: Rectovaginal Fistulas at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2967329/
