Neuromuscular Junction
What is Neuromuscular Junction?
A synapse refers to the space between the skeletal muscle cell and motor neuron. Neuromuscular junction is a type of synapse or connection between the skeletal muscle and motor neuron that acts like a bridge to transmit signals. It is also referred to as neuromuscular myoneural. When a signal passes through this space, the motor neuron stimulates skeletal muscles to contract. Human brain has numerous connections of such types2, 3.
Structure of Neuromuscular Junction
Neuromuscular junction comprises of neuron and skeletal muscle cell. When a neuron combines with a motor neuron, it is referred to as spinal motor neuron. Motor neuron arises from the spinal cord and communicates nervous energy to arouse skeletal muscle fibers. This communication occurs through axon which is a small protrusion of a nerve cell that transmits information to muscles, glands and organs.
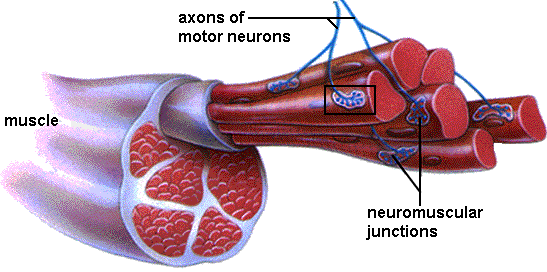
Features of NMJ
This junction has the following characteristic features:
- The junction comprises of two membranes called post and presynaptic membranes. Presynaptic membrane is used to send impulses carried by neurotransmitter chemicals. This membrane contains mitochondria, neurotransmitters and other cell organelles. Post synaptic membrane is used to receive the nerve impulses and consists of neuroreceptors. There is a small gap between these membranes called synaptic cleft.
- There are small spherical vessels at the junction that contain neurotransmitters.
- There is also a very thick post synaptic membrane which has receptors that bind chemical substances which transmit the signal from pre synaptic membrane.
Disorders of Neuromuscular Junction
Neuromuscular junction can fail to work properly due to disorders such as
Eaton-Lambert syndrome
This is an autoimmune disease that affects communication between your nerves and muscles which leads to muscle weaknesses. Nerves communicate with muscles by producing neurotransmitters which interact with neuroreceptors at the neuromuscular junction. Eaton- Lambert syndrome occurs when the body’s immune system produces antibodies that attack nerve endings that regulate the amount of acetylcholine in your body. Acetylcholine is a type of neurotransmitter that stimulates muscles to contract. When muscles contract, they enable you to make movements such as walking, shrugging your shoulders, etc.6
In many cases, your immune system attacks a protein called voltage gated calcium channel (VGCC). This protein releases acetylcholine. When this protein is attacked, acetylcholine will not be released which in turn affects your muscles to work properly by weakening them.
Research has shown that Eaton-Lambert syndrome is linked to some cancers such as lung cancer. Some researchers believe that cancer cells produce voltage gated calcium channel protein. In this case, your immune system produces antibodies against this protein and the attacks both muscle and cancer cells in your body. People with lung cancer are at higher risk of developing Eaton-Lambert syndrome although anyone can get this disorder during their lifetime.
The most common symptom of this disorder is muscle weakness which affects your ability to move. This weakness generally occurs in your legs and arms. People with muscle weaknesses have difficulties walking, climbing and getting up on the chair. In addition people get tired easily. Other symptoms include dry mouth, eyelids hang down and people may experience pain in the arms and thighs. Men may have erectile problems.
Myasthenia Gravis
This is an autoimmune disease that causes skeletal muscles to become weak. This disease occurs when your body releases antibodies that attack and destroy muscle receptor sites for acetylcholine. When these receptor sites are damaged, your muscles receive fewer nerve signals or none at all which makes muscles to become weak.1
These antibodies can also inhibit the function of a protein known as a muscle-specific receptor tyrosine kinase. This protein is responsible for forming nerve- muscular junction. When this protein is blocked, it may lead to myasthenia gravis.
Other causes of this condition include genetic factors. Mothers with myasthenia gravis have children born with this condition although it is not common. Studies also say that children with congenital myasthenic syndrome, an inherited form of myasthenia can also develop this condition.
There are also factors that can worsen myasthenia gravis such as
- Having stress
- Using medications such as beta blockers, quinidine sulfate and phenytoin.
Having this condition can also lead to other complications such as myasthenic crisis. Myasthenic crisis is a very serious condition that happens when your muscles that regulate breathing become weak and unable to work properly. This requires urgent medical attention to help a person breathe properly.
Stiff person syndrome
It is a neurological disorder with features of autoimmune disease. This disease is characterized by muscle stiffness in the limbs and trunk. Although the real cause of this disease is not known, scientists have linked it to an abnormal immune response in the brain and spinal cord. The body produces antibodies against a protein called glutamic acid decarboxylase which is responsible for making gamma-aminobutyric acid that control how muscles move.4
Stiff person syndrome is also associated with other immune diseases such as vitiligo, thyroiditis, diabetes etc. It affects women more than men. People with this condition have difficult to walk and are affected by any noise which can stimulate muscle spasms and falls.
Diagnosis of NMJ Disorders
Disorders affecting neuromuscular junction can be diagnosed through the following:1, 3
Physical exam
Your doctor assesses your symptoms and past health record to understand this condition. Your doctor then performs neurological examination by testing the strength and tone of your muscles, balance, coordination and your sense of touch and sight.
Edrophonium test
Your doctor edrophonium chloride in your vein so as to diagnose these disorders. When you feel a sudden improvement in your muscle strength, it is an indication that you a neuromuscular disorder.
Ice pack test
Your doctor can also use this test if you have drooping eyelids. In this test, your doctor puts a bag with ice pack on your eyelids for some time and removes them to assess the symptoms.
Blood analysis:
Your doctor can also conduct analysis on a sample of your blood to determine presence of abnormal antibodies.
Electromyography (EMG)
Your doctor can also determine electrical activity of signals passing though your brain and muscles using electromyography test. In this test, your doctor inserts a wire electrode via your skin into the muscle to test a muscle fiber.
Other tests that can be conducted include pulmonary test to determine how you are breathing. Imaging scans are also conducted if you are suspected to have a tumor in thymus gland.
Treatment of NMJ Disorders
Most of these disorders have no cure; treatment focuses on relieving their symptoms. The following are some treatment options for these disorders:1
Medications
Your doctor can prescribe medicines to improve communication between your nerves and muscles such as pyridostigmine. These drugs boast the strength and contraction of muscles. These drugs may lead to nausea and excessive sweating.
Other medicines that are recommended include those that may change or inhibit your immune system from producing antibodies. In some cases, intravenous immunoglobulin can be injected in veins to change your immune system.
Surgery
In case you have a tumor in the thymus gland, your doctor will conduct surgery to remove it.
Reference List
- Myasthenia gravis. Available at http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/myasthenia-gravis/home/ovc-20200259
- http://www.newhealthadvisor.com/Neuromuscular-Junction.html
- Neuromuscular junction disorders. Available at http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/brain,-spinal-cord,-and-nerve-disorders/peripheral-nerve-disorders/overview-of-neuromuscular-junction-disorders
- Stiff person syndrome. Available at https://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/5023/stiff-person-syndrome
- http://study.com/academy/lesson/the-neuromuscular-junction-function-structure-physiology.html
- Eaton-Lambert Syndrome. Available at http://www.merckmanuals.com/home/brain,-spinal-cord,-and-nerve-disorders/peripheral-nerve-disorders/eaton-lambert-syndrome
