Blocked Salivary Glands
What are Blocked Salivary Glands?
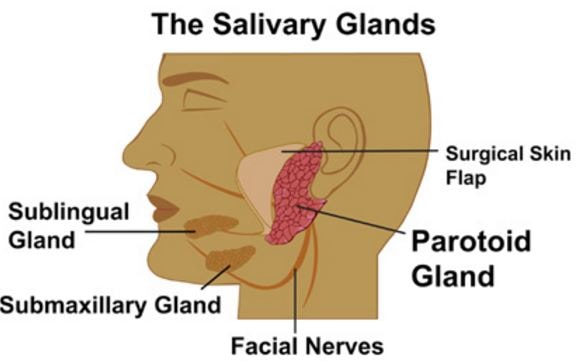
Salivary glands are masses that are grouped for the production of the saliva in order to help the process of digestion. These glands are present around the oral cavity.
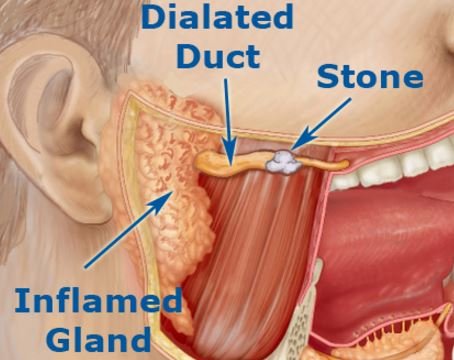
Upon the saliva blockage, it will make the saliva accumulate and cannot pass freely due to a painful swelling. When a stone or duct forms in the salivary glands, this will cause a blockage on the flow of saliva in the mouth. Most people who have this condition do not only have a single stone, but instead they have multiple stones.
The majority of the stones found at the floor of the mouth have an effect on the submandibular glands. The other two glands; sublingual and parotid glands, are less common to be affected. Any uncommon problems in the throat might cause a big impact to the person’s hygiene and digestion. Today, the blocked salivary glands are one of the conditions that is outlined and most talked about.
What are the Symptoms?
In many cases, symptoms for blocked salivary glands do not show and sometimes, individuals having this condition are not even aware that they have it. Some physicians discover the condition through an X-ray for some other reasons. Unless the stones reach a certain size and hinders the duct, the salivary the gland poses problems resulting to some symptoms. These are:
- Having difficulty in swallowing and even opening the mouth
- Redness on the infected area
- Pain that goes on and off and sometimes the pain becomes really serious especially during or before meals
- Dry mouth
- Swelling of the gland that has been affected
- Bad breath
- Having a hard time chewing food
- Tenderness and inflammation of the neck, face, or mouth
- Fever
What Causes it?
Salivary stones form when the gland is assembled by chemicals in the saliva that most-likely contains calcium and other salts. Stones range in size from 1mm to 10mm.
Smaller stones can block the flow of the saliva but it could not always impede the process of salivary production.
Males and females can develop this condition but ages 40 and above are more susceptible to it. The precise rationale on why the salivary stones form is still a mystery, but there are risk factors that grants the decreasing of saliva production and saliva that has been condensed. These factors are:
- Distressed salivary glands
- Lack of fluids in the body
- Too much sun exposure
- Surgery of the mouth or throat can also be the reason of the blockade
- Eating a little amount of food or not eating at all during meals
- Other health issues or conditions that may result to the formation of stones
- Medications that lessens the production of saliva in the glands
How to treat?
Before any treatments are done, the physician will either do a physical examination, CT scan, ultrasound or X-ray in order to check the stones. If there are any stones cited, the physician’s goal is to help the patient get rid of it.
For small stones, the dentist or the physician may recommend to suck a lemon that is sugar free and drinking lots of water afterwards to trigger the saliva to flow and causes the stones to pass automatically. If the stones are much larger which is also more difficult to remove, physicians make a small cut in the mouth to take the stone out.
Antibiotics are also prescribed by physicians if an infection is present. There is also another technique to get rid of the stones and it is Sialendoscopy. The process is to locate the stone first with a tiny lighted scope and then with the help of micro instruments, the physician can remove the stone. For individuals who develop the stones frequently or if the other previous treatments failed, surgery is necessary.
Home Remedies
If the blocked salivary glands are not very severe, home remedies can help. Below are some remedies:
- Warm compress. This can help increase the flow of saliva for pain relief and eventually getting rid of the stones.
- Salt water. Mix salt with warm water and gargle it to eliminate inflammation and pain.
- Ginger soup
- Drink lots of water and avoid too much exposure to the sun to lessen the chance of developing salivary stones.
Surgery
If the salivary stones are too large, a surgery is recommended by the physician in order to remove it. A gland will be removed but two glands will be left, therefore there is still enough saliva produced.
Before the person goes on with the surgery, everything should be talked out with the physician since there are some nerves which control the movements of the face that might be trimmed. The movements of facial muscles will be affected after the surgery is done.
References:
Blocked Salivary Gland risk factors, diagnosis, treatment at http://www.healthcare-online.org/Blocked-Salivary-Gland.html
http://www.healthline.com/health/salivary-duct-stones#Overview1
http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/salivary-gland-stones-symptoms-causes-treatments
Tucker MR (2008). Contemporary oral and maxillofacial surgery (5th ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: Mosby Elsevier. pp. 398, 407–409.
Capaccio, P; Torretta, S; Ottavian, F; Sambataro, G; Pignataro, L (August 2007). “Modern management of obstructive salivary diseases.”. Acta otorhinolaryngologica Italica : organo ufficiale della Societa italiana di otorinolaringologia e chirurgia cervico-facciale 27 (4): 161–72.
Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CA, Bouquot JE. (2002). Oral & maxillofacial pathology (2nd ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. pp. 393–395.
